|
What
Causes Plates to Move? |
|
|
 1 They say a
watched pot never boils. But do you know what happens when a pot of water does
boil? The water is hotter near the bottom where the heat source is located. The
cooler water on top sinks to the bottom. The hotter water on the bottom is
pushed to the top. This is a kind of convection current.
1 They say a
watched pot never boils. But do you know what happens when a pot of water does
boil? The water is hotter near the bottom where the heat source is located. The
cooler water on top sinks to the bottom. The hotter water on the bottom is
pushed to the top. This is a kind of convection current.
2 Scientists think convection
currents are what cause earth's plates to move. A convection current is caused
by differences in temperature. Mantle material close to earth's core is very
hot. Mantle material near the lithosphere is cooler.
3 The cooler, denser material
sinks toward the core. The hot material near the core expands and becomes less
dense. It rises and takes the place of the cooler material. The sinking
material becomes hotter and rises. This is a continuous circular motion.
4 Earth's convection currents
can be thousands of kilometers across. But they move very slowly. They flow at
rates of a few centimeters per year. Scientists believe this movement of mantle
material carries the plates of the lithosphere with it. It causes the plates to
move.
5 The rising material in this
convection current spreads out. It pushes the plates upward and outward. These
are divergent boundaries. The material moving downward in the current pulls the
plates down with it. These are convergent boundaries.
6 The plates of the
lithosphere are made of two different types of crust. Most contain both oceanic
and continental crust. Only the Pacific plate contains just oceanic crust. As
the plates move, these different types of crust cause different events.
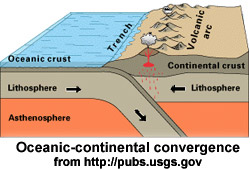
7 Oceanic crust is denser
than continental crust. As an oceanic plate bumps into a continental plate, the
oceanic plate moves under the continental plate. The oceanic plate is
subducted. It is forced down into the trench. The continental plate is folded
upward.
8 Two continental plates have
the same density. When they collide, neither plate is forced downward. The
edges of these plates fold upward. Mountains are formed.
9 When two oceanic plates run
into each other, one is forced under the other. This forms a deep trench. The
crust of the subducted plate melts. The magma flows upward. Volcanoes are
formed.
10 Plates move in different
directions and at different speeds. These differences cause other events to
occur. Scientists believe that they sometimes run together and form one large
plate. Other plates break apart. Still others might be subducted into a trench
and disappear.
11 What does all this plate
movement mean for our earth? Scientists believe that more than 500 million
years ago, the land masses were many different small fragments. Later they
moved together to form one large mass. This was the continent Wagener called
Panagea. It was surrounded by one large ocean.
12 Scientists believe this
large mass then broke into two large continents. Over time they broke apart
into the continents we know today. Many scientists think that the continents
are moving at a rate of one to five centimeters per year.
13 In about fifty million
years, the Atlantic and Indian Oceans will become larger. The Pacific will
shrink. Africa and Australia will join Asia once again. If this happens, the
earth will look very different than it does today.
Copyright © 2008 edHelper
|
Name _____________________________ |
|
|
Date ___________________ |
What Causes Plates to Move?
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
What Causes Plates to Move? - Answer Key |
1 Differences
in temperature
2 ![]() Large
and slow-moving
Large
and slow-moving
3 ![]() Subduction
Subduction
4 ![]() Mountains
Mountains
5 ![]() Trench
Trench
6 They will join together again.
